Are You Drinking Plastic With Your Morning Coffee?
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you purchase a product through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Check out our complete Replace Plastics Top Picks for more eco-friendly alternatives.
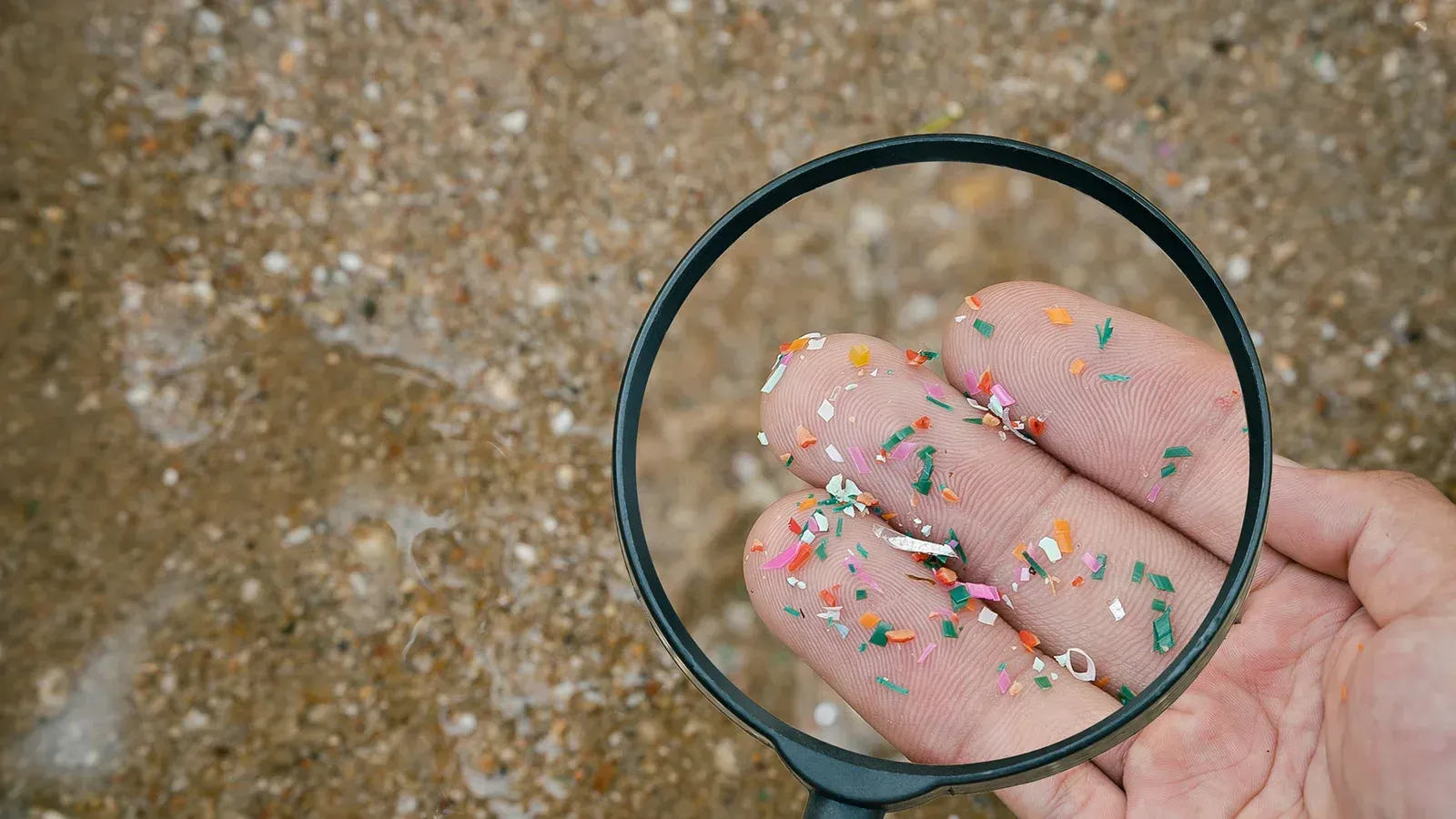
Your morning cup of coffee might be more than just a caffeine fix; it could be a source of harmful forever chemicals and microplastics. While this news may sound discouraging, there are simple swaps you can make to reduce your exposure and enjoy your coffee in a healthier way. Let’s dive into the ways you can transform your coffee routine and protect your health.
Table of Contents
- The Problem with Plastic in Coffee
- Easy Swaps for a Healthier Brew
- Additional Considerations for Your Coffee Routine
- FAQs
- Start Your Plastic-Free Coffee Habit Today!
The Problem with Plastic in Coffee
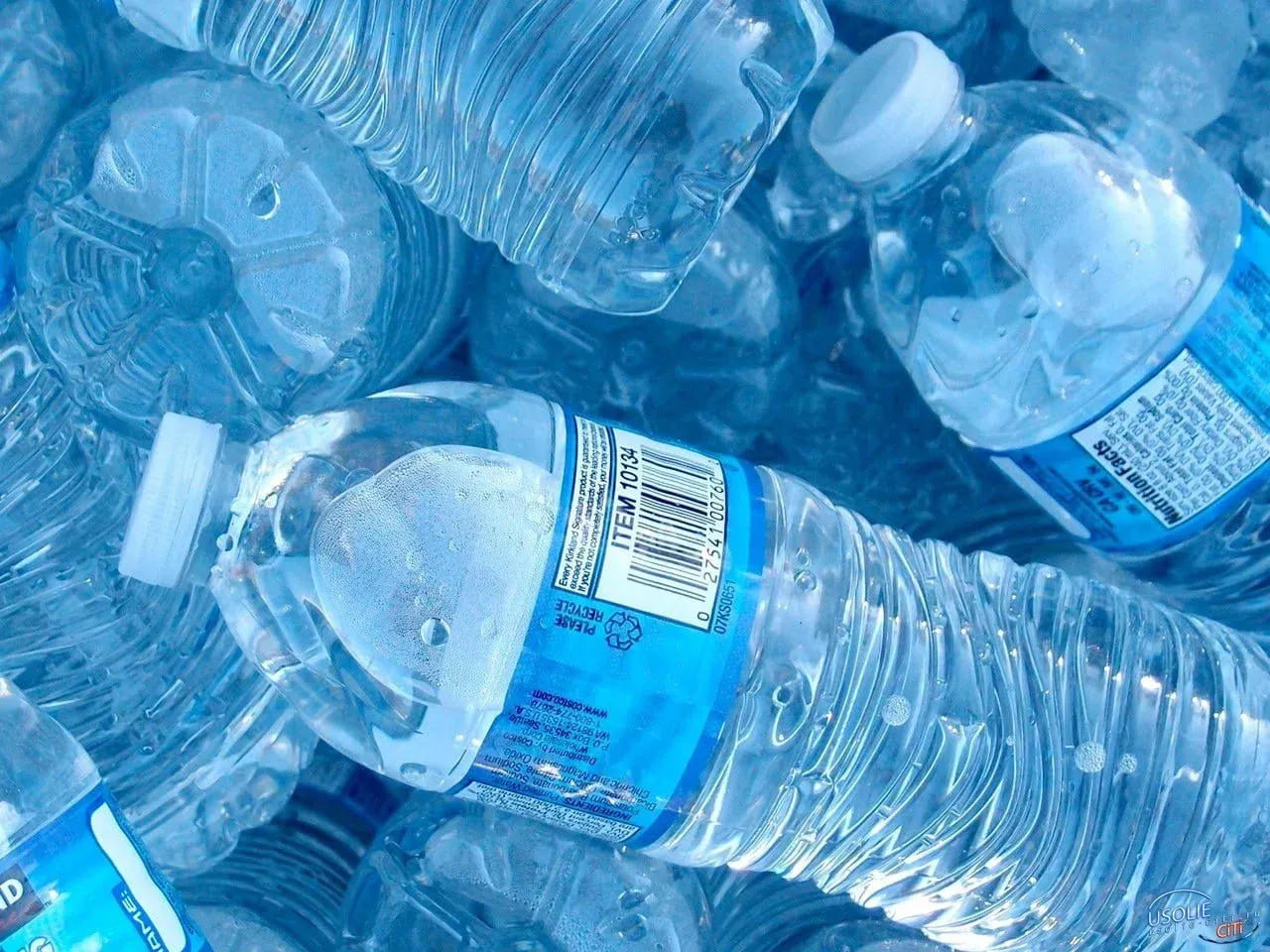
Many of us rely on convenient coffee options like K-Cups and disposable coffee cups, but these products often contain plastic that leaches harmful substances into your drink. Studies have shown that microplastics and “forever chemicals” can seep into your coffee, especially when hot liquids are involved. This is concerning because these chemicals have been linked to various health issues.
Easy Swaps for a Healthier Brew
The good news is that making healthier choices doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some easy swaps you can implement to significantly reduce your plastic exposure while enjoying your coffee.
1. Ditch the K-Cups
K-Cups are convenient but come with a hefty plastic price tag. Instead, consider using stainless steel pods that you can fill with your own coffee grounds. This not only eliminates plastic waste but is also more cost-effective in the long run. You can find these stainless steel pods on platforms like Amazon.
If you still love the convenience of pre-packaged coffee, look for brands like Beaniac, which offers biodegradable vessels made from materials other than plastic. This way, you can enjoy your coffee without the guilt of contributing to plastic pollution.
Check Out Our Plastic-Free Alternative Top Picks!
2. Switch to Drip Coffee
Drip coffee makers are another option, but be mindful of the plastic components involved. Instead of using plastic filters, you can opt for stainless steel replacements that fit into your existing coffee maker. This simple change can drastically reduce the amount of microplastics leaching into your drink.
3. Try a Pour-Over Method
If you have a bit more time to enjoy your coffee, consider using a pour-over system. This method can enhance the flavor of your brew and allows you to control the process fully. While it may take longer, many coffee enthusiasts find it worth the effort. Just make sure to use unbleached cotton filters or a reusable filter to avoid any unwanted chemicals.
4. Rethink Your Coffee Filters
Many white coffee filters contain forever chemicals that prevent them from breaking down. Instead, switch to reusable filters made from cotton or stainless steel. This not only reduces your plastic exposure but is also better for the environment. You can easily rinse them out and reuse them daily.
5. Avoid Disposable Coffee Cups
Think twice before grabbing that disposable coffee cup from your favorite café. While they may appear to be made from paper, they are often lined with polyethylene, a type of plastic. These cups can take decades to decompose and release harmful chemicals into your drink.
Instead, invest in a stainless steel or ceramic travel mug. Many coffee shops will allow you to bring your own cup, and some even offer discounts for doing so. It’s a win-win situation!
See Out Our Top Plastic-Free Coffee Essentials!
Additional Considerations for Your Coffee Routine
As you transition to a more sustainable coffee routine, consider the following tips:
- Check Your Coffee Maker: If you have a plastic coffee maker, consider switching to a glass or stainless steel model to avoid leaching chemicals.
- Mind Your Lids: If you do use disposable cups, avoid the plastic lids. Opt for a reusable lid or a cup that comes with a safer alternative.
- Stay Informed: Keep track of new studies and information regarding microplastics and coffee. Knowledge is power in making healthier choices.
FAQs
What are forever chemicals?
Forever chemicals are substances that do not break down in the environment and can accumulate in the human body over time. They are often found in various consumer products, including food packaging.
How can I tell if my coffee products contain plastic?
Check the packaging and product descriptions for terms like “BPA-free” or “free of phthalates.” However, be aware that many products may still contain microplastics even if they are labeled as such.
Are there any health risks associated with microplastics?
Research is ongoing, but studies suggest that microplastics may be linked to health issues such as hormonal disruption, inflammation, and other chronic conditions.
What is the best way to make coffee without plastic?
The best way to make coffee without plastic is to use a pour-over system or a drip coffee maker with stainless steel components and reusable filters. Always avoid plastic containers and disposable cups.
Start Your Plastic-Free Coffee Habit Today!
Making small changes to your coffee routine can lead to significant health benefits and a reduced environmental impact. By swapping out plastic products for more sustainable options, you can enjoy your coffee guilt-free. Start your microplastic detox today and encourage others to join you on this journey towards a healthier lifestyle.
Want more tips on cutting down plastic and living sustainably? Check out our other blog posts for easy, actionable ways to make a difference in your everyday life. Small changes, big impact!